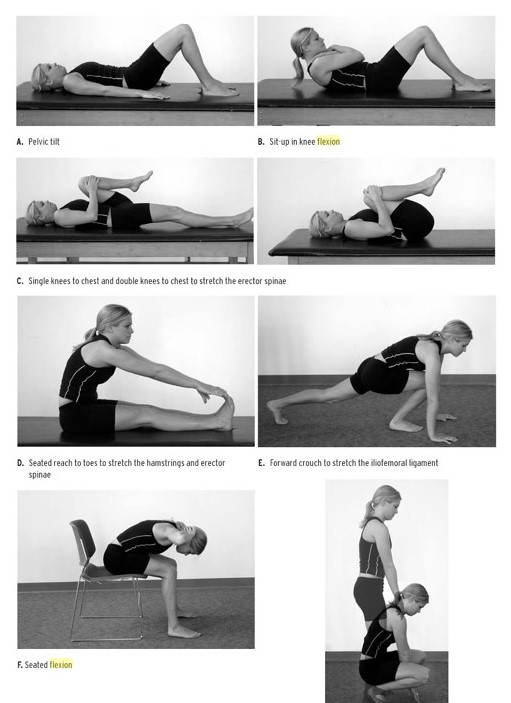
Enhance your health with free online physiotherapy exercise lessons and videos about various disease and health condition
The Valsalva Maneuver
Valsalva maneuver - A forceful exhalation against a closed airway that increases pressure in the thoracic cavity and results in decreased venous return.
During resistance training, individuals often hold their breath to generate greater force. This results in increased intra-abdominal and intrathoracic pressures, which limits venous return and subsequently does not significantly alter EDV (end-diastolic volume). This mechanism of enhancing force-generating capacity is referred to as the Valsalva technique.
The Valsalva Maneuver
The Valsalva maneuver, a natural response to lifting heavy loads, is characterized by a forced exhalation against a closed glottis. During forced exhalation, a sudden increase in intra-abdominal and intrathoracic pressures is produced by the contractions of the abdominal and respiratory muscles. Elevated pressures compress the blood vessels within the chest cavity, leading to a decrease in venous return and CO. In addition, compression of the aorta leads to stimulation of the baroreceptors, producing a reflex-induced bradycardia to compensate for the increased pressures. Aortic pressure subsequently rises, stimulating sympathetic activity. HR and BP rise in response to maintain CO and perfusion. At the cessation of the forced exhalation, venous return rapidly increases, intra-abdominal pressures drop, and CO is increased, dramatically increasing the mechanical load on the heart. The Valsalva maneuver can be dangerous due to the sudden and abrupt changes in BP. These dramatic changes in HR, BP, and CO may produce symptoms including dizziness, light headedness, and syncope.
However, the Valsalva technique can help protect against injury during heavy weight lifting. The supporting ligaments of the spine can only support 4 to 5 lb of pressure before failing.5 Therefore performing the Valsalva maneuver during heavy lifts, such as the Roman dead lift, squats, bench press, and clean and jerk, assists core musculature in supporting the spine and decreases the compressive load on the intervertebral discs.
Strength and conditioning coaches often recommend the Valsalva technique during weight-lifting exercises requiring a stable core. Individuals are coached to perform the maneuver during the work phase of the lift. Individuals should inhale before the exercise, hold their breath through the most difficult phase of the lift, and exhale to complete the lift. Because the consequences of improper breathing with weight lifting can be severe, proper education is essential.
Valsalva technique in Women's Incontinence Exercise
Usually, women do not notice improvement in incontinence for the first 6 to 8 weeks of an exercise program.This may be too discouraging for some. Physical therapists should take care to note that 30% of women are unable to contract their pelvic floor muscles voluntarily.Performing the exercise improperly can have an undesired effect by increasing intra-abdominal pressure. Many women actually bear down by holding their breath and performing a Valsalva's maneuver or substitute for the appropriate muscle contractions by contracting muscles in the thighs or buttocks. Consequently, mere verbal or written instruction may be inadequate preparation to undertake a home program, which is sometimes known by some patients and health professionals as a Kegel exercise program. PMEs are often called Kegels, named for the obstetrician who performed the seminal research that postulated that pubococcygeus muscle activity provides critical support for the bladder.
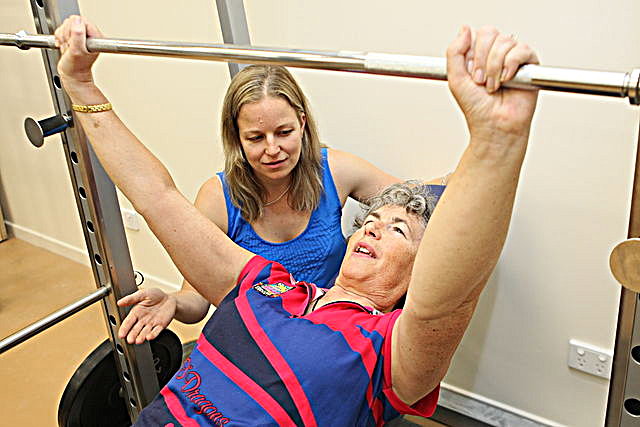
Valsalva technique in Elderly People
Read more about Valsalva on PubMed
Appropriate precautions should be followed when using exercise with elderly individuals. Severe osteoporosis may even pose limitations for ROM exercises. Older hypertensive individuals who perform a Valsalva's maneuver during strenuous resistive exercise risk a dangerous elevation in blood pressure. Exercise-induced muscle damage and soreness occur especially after vigorous eccentric exercise in both young and old subjects. Although rates of tissue repair are similar for healthy active subjects, older subjects show significantly greater muscle shortening. This may predispose the older individual to a greater risk of further injury from exercise.
Return from Valsalva Maneuver to Home Page
Recent Articles
|
Author's Pick
Rating: 4.4 Votes: 252 |

