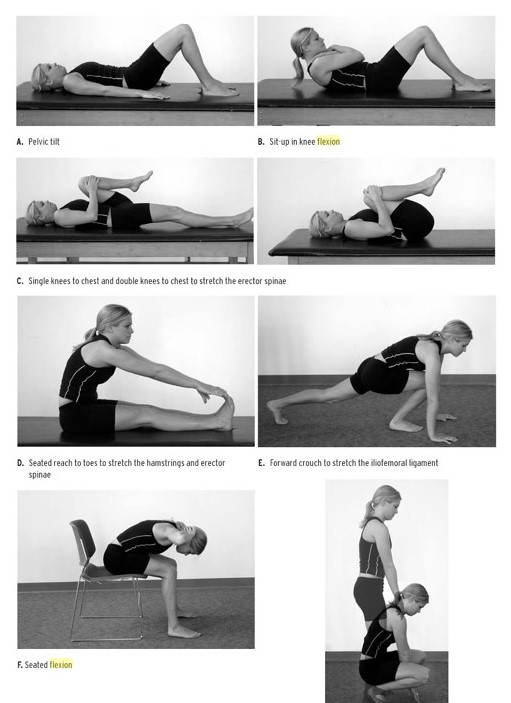
Enhance your health with free online physiotherapy exercise lessons and videos about various disease and health condition
Mat activities
Mat activities are one of the most important parts of rehabilitation programme of SCI patients. Mat exercises are included in the treatment programme as soon as weight bearing to spine is permitted.
Mat activities are given to:
- Facilitate balance
- Promote stability
- Mobilize and strengthen the trunk and limb.
- Train for functional activities
To achieve the desired effect of the treatment programme, mat activities should be sequenced from easier to difficult and progression through sequence should be considered. The type of the mat activities, given to the patient is determined by the therapist on the basis of level of lesion and medical status of patient. The limit to which an activity can be performed and time taken to learn it depends on the ability of the patient. But therapist should work hard to improve the timing and speed of the patient.
Different mat activities taught to patient are:
a) Rolling
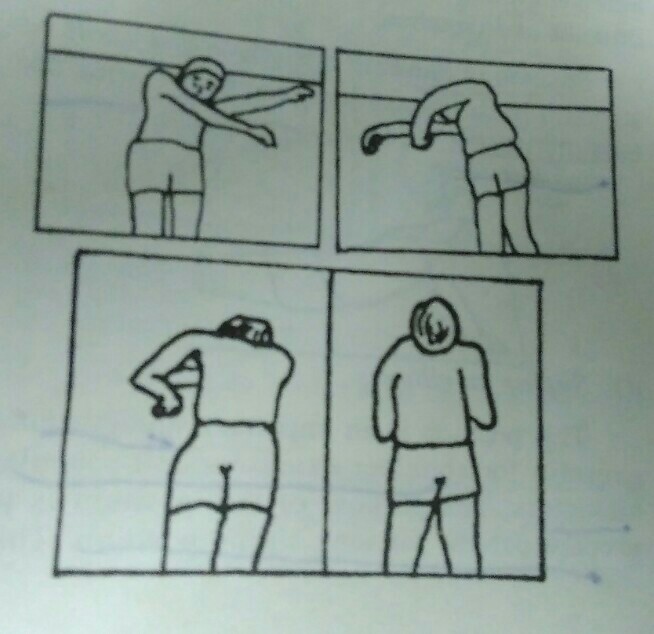
For rolling to be effective, patient is required to learn to move the head, neck, upper limb, lower limb and trunk in a balance manner. Rolling is needed to improve bed mobility and to change position independently. Initially, rolling is taught to patient in mat but afterwards patient gets confidence to perform it over bed.
Action to role prone from supine position:
- 1) Patient lies in supine position.
- 2) Patient flexes his head, neck and right shoulder.
- 3) Right arm is moved towards left side to create momentum.
- 4) The momentum of arm is transferred to trunk and lower limb.
- 5) The lower half of body will be rolled to prone position. Flexion of hip and knee will facilitate the roll.
- 6) Patient takes his right shoulder at the back side by putting weight on left forearm and thus, weight is distributed on both upper limb.
- 7) Patient lies prone.
Rolling to prone can also be assisted by use of pillows under one side of pelvis or scapula if needed. The number of pillows is decreased in progression.
b) Prone on elbow
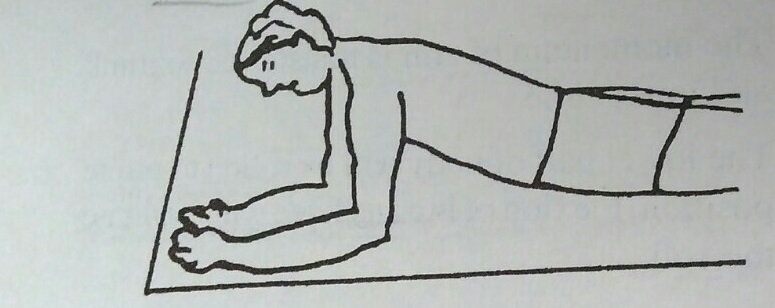
This position on mat activities given to cervical lesion patient facilitates head and neck control and strengthens serratus anterior and other scapular muscles. This position is very important to train the patient to gain stability is quadruped and sitting position. Prone on elbow position should be used carefully in lumbar injuries as this increases lumbar lordosis.
Action of patient:
- 1) Patient lies prone and places his elbows close to trunk.
- 2) Elbows are pushed down while lifting head and upper trunk.
- 3) Now, patient brings the elbow to the level of shoulder and body weight is shifted through elbows.
c) Prone on hands
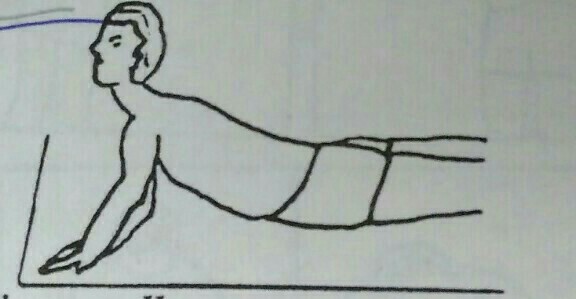
This position is given to paraplegic patient because it requires strong pectoralis major and deltoid muscles. However, this activity is not appropriate to all paraplegics as excessive lordosis is produced. Prone on hand position is required to gain postural alignment during standing, ambulation and standing from floor with use of orthosis and crutches.
Position of hands in this position is same as standard push up position except that arms are laterally rotated.
d) Supine on elbow
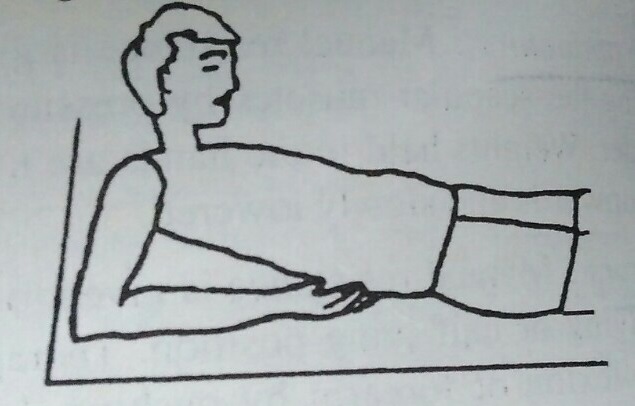
This position is an important strengthening exercise for shoulder extensors and scapular adductors. The purpose of this position is to prepare patient for long sitting position. This position is assumed according to the comfort and disability of patient.
This position is achieved either from side lying position or by pushing the elbow over mat and lifting into this position. The later technique requires a strong abdominal muscle.
e) Pull ups
This kind of mat activities is given in quadriplegics to strengthen their biceps and shoulder flexors, which may be required for wheel chair propulsion.
Action:
- 1) Patient lies supine.
- 2) Therapist stands over the patient in high kneeling position.
- 3) Lower limb of therapist is near the hips of patient.
- 4) Patient holds the forearm of therapist and pulls himself to sitting position and then lowers down.
f) Sitting
Sitting position are important for various activities in daily life such as ADL, transfer, dressing, wheel chair mobility etc. Sitting is achieved easily by paraplegics, but it is ac difficult job for quadriplegics.
Stability in sitting position for quadriplegics is achieved by weight bearing through hands with flexed fingers, extended wrist, extended elbow and hyper extended and externally rotated shoulder.
Sitting position varies according to level of lesion.
To sit from supine position in lower level lesion:
- 1) Patient lies in supine position.
- 2) Patient turn the upper trunk to left side moving the right arm toward left side of body along with head and neck flexion.
- 3) Both elbows are brought nearer to trunk alternately.
- 4) Patient learns over left elbow and extends the right arm behind the body.
- 5) Left elbow is extended by leaning over right arm.
- 6) Both hands are brought forward alternately to achieve sitting position.
To sit from supine position in upper level lesion:
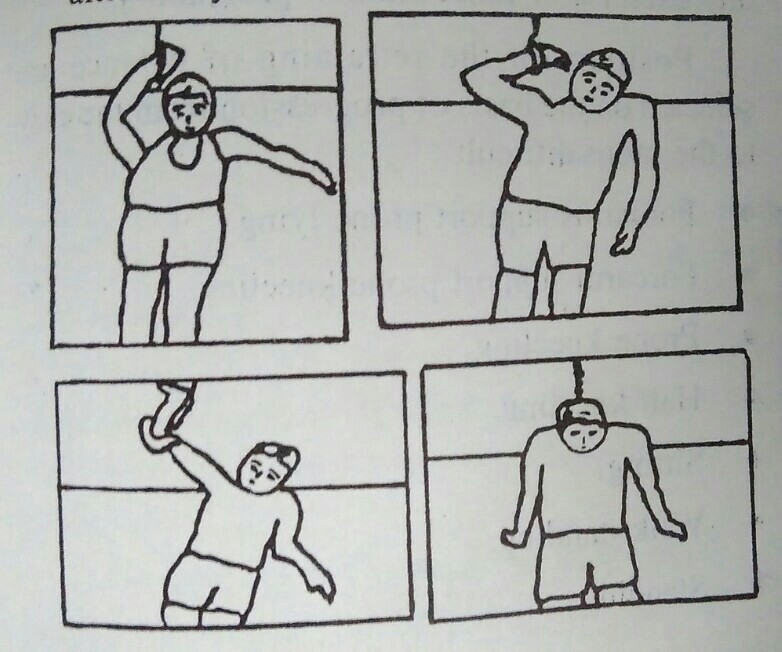
In high level lesion, patient demonstrates poor sitting posture. Some patient with spared muscles of upper limb may achieve sitting position with the help of monkey pole.
Position of monkey pole:
Monkey pole is suspended over the midline of body or towards the supporting arm. The handle of pole should reach the patients extended wrist.
Action of patient:
- 1) Patients hook the extended wrist of one arm (right) in the pole.
- 2) By leaning on the left elbow, body is pulled towards pole.
- 3) Flex the right elbow on monkey pole.
- 4) Bring the left elbow closer to trunk by distributing weight through right elbow.
- 5) Now, support body weight on the left elbow by leaning over left side.
- 6) Take right arm out of pole and extend the arm behind body by externally rotating the shoulder.
- 7) Transfer weight over right arm and extend the left elbow with weight over hand.
- 8) Move both hands forward to same level alternately.
- 9) The sitting position is gained.
g) Lifting
Lifting is done to relieve continuous pressure over body part. Lifting from sitting position requires a great balance in sitting position.
Action:
- 1) Patient sits in long sitting position.
- 2) Hands are placed on mat with elbows extended
- 3) Patient pushes down the hands, depresses shoulder and lifts the buttocks off the ground.
Movements in mat can be achieved by different lifting technique.
To lift sideways: (With lesion below C6 without triceps, only pectoralis major partially innervated)
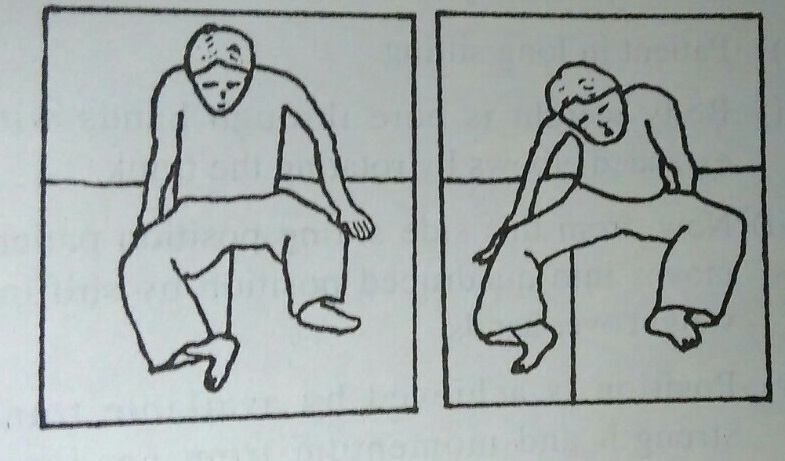
Action of patient:
- 1) Patient in sitting position.
- 2) Places both hands with extended elbow on mat. One hand is close to hip band other one is placed approximately one foot away. Forearm is supinated.
- 3) Now flex the body little more and lift the buttocks.
- 4) At the same time, twist the head and shoulder towards the opposite side of move.
- 5) Now, move the pelvis towards the hand lying far from body.
To lift forward
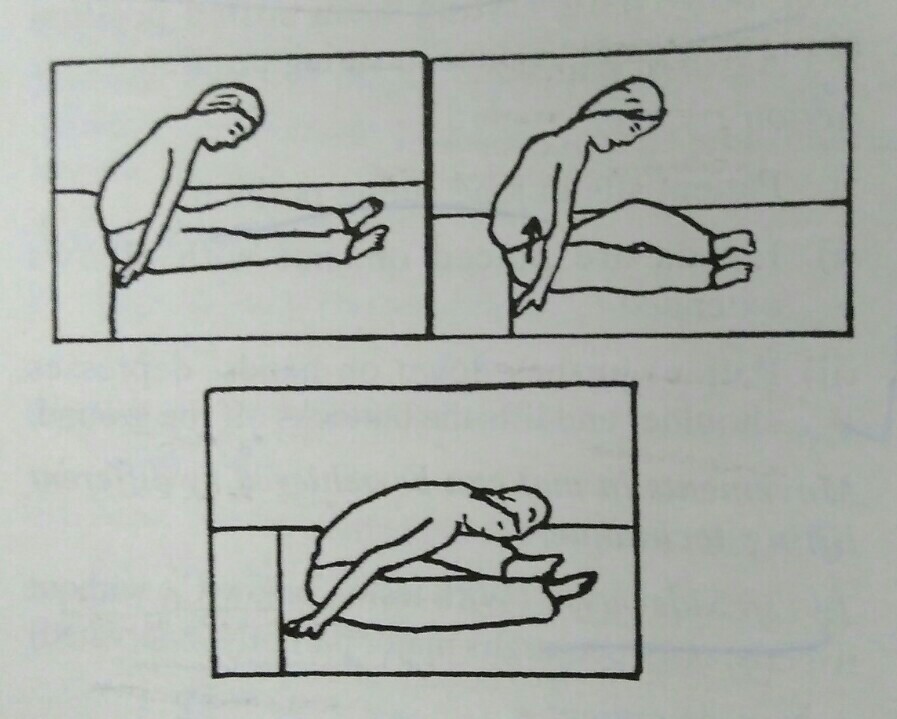
- 1) Patient in sitting.
- 2) Patient flexes his trunk so that head lies over knees.
- 3) Both hands are placed close to the body slightly in front of the hip joint.
- 4) Elbows are extended and forearm supinated.
- 5) Now, distributing body weight through hands pull the buttocks forwards.
h) Quadruped Position
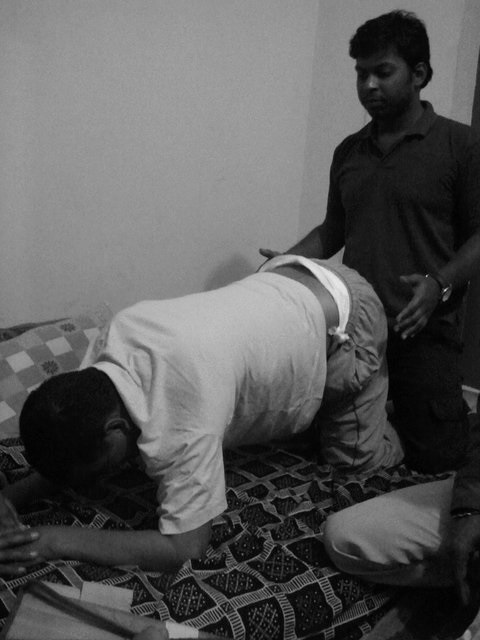

In this position, trunk lies horizontal to ground and body weight is distributed over both hands and both knees. It is also called as prone kneeling position. This is the first sequence in mat activities that allow weight bearing through hips.
This position helps to initiate control of muscle of lower trunk and hips. This position can either be achieved from prone on elbow position or from long sitting position.
To assume position from long sitting:
- 1) Patient in long sitting.
- 2) Body weight is bore through hands with extended elbows by rotating the trunk.
- 3) Now, from the side sitting position patient moves into quadruped position by shifting weight over hands.
- 4) Position is achieved by available trunk strength and momentum from head and shoulders.
i) Kneeling (Paraplegia)
It is more difficultly to manage for patient with instability at trunk. In this position, centre gravity is raised, base is small and gravity falls near the edge of the base. This position is important to promote upright balance control. This position is best achieved from quadruped position.
Position of patient
- Patient is in quadruped position.
Position of therapist
- Falls of patient in kneeling position.
Action of patient
- Patient moves the hand backward towards knees in prone kneeling position.
- Knees are further flexed.
- Pelvis is dropped towards heel.
- Patient sits on heel.
- Patient supports his upper limb on therapist’s shoulder.
- By thrusting with his upper limb and extending his neck and hips, patient rises himself to kneeling position.
Action of therapist
Therapist manually guides the pelvis.
SCI Related Pages
Further Reading for mat activities for SCI
- Jones ML, Harness E, Denison P, Tefertiller C, Evans N, Larson CA. Activity-based Therapies in Spinal Cord Injury:: Clinical Focus and Empirical Evidence in Three Independent Programs. Topics in Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation. 2012;18(1):34-42. doi:10.1310/sci1801-34.
- How To Control Trunk Balance & Mat activities- Apparelyzed Spinal Cord Injury and Cauda Equina Syndrome Support Forum
- Spinal Cord Injury and Exercise- NCHPAD
Return from Mat activities to SCI Rehab
Return from Mat activities to Home Page
Recent Articles
|
Author's Pick
Rating: 4.4 Votes: 252 |