Enhance your health with free online physiotherapy exercise lessons and videos about various disease and health condition
Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome
Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome is an overuse problem that results from inflammation and irritation of the distal portion of the iliotibial tendon as it rubs against the lateral femoral condyle.
What Is Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome ?
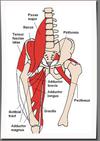
The iliotibial band is a non elastic collagen cord stretching from the pelvis to below the knee. At the top it is attached to the iliac crest where it blends with gluteus maximus and TFL.
As the tract descends the lateral side of thigh its fibres attach to the linea aspera of the femur.The superficial fibres continue downwards to attach to the lateral femoral condyle, lateral patellar retinaculum and anterolateral aspect of the tibial condyle.
In standing, the itb lies posterior to hip axis and anterior to knee axis and therefore help to maintain hip and knee extension, reducing the muscle work required to sustain an upright stance. As the knee flexes to 30 degree, the itb passes posterior to knee joint axis and in doing so it glides over the lateral femoral condyle.

When the tendon passes the knee (lateral femoral condyle) there is a bursa sac between the bone and the tendon.This tendon moves over a bony bump at the outer knee as it passes in front and behind it.The bursa functions like a water balloon to reduce friction.In IT Band Friction Syndrome, overuse causes excessive friction at this bump, resulting pain and inflammation of the bursa (bursitis),tendon (tendinitis)or both.
What Causes Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome?
IT Band Friction Syndrome is caused by excessive friction of the iliotibial band and the underlying bursa due to repetitive knee bending activities. This is an overuse injury, although direct trauma to the outer knee may cause the bursa to get inflamed.
Factors that contribute to the development of Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome-
- Cavus feet
- varus knee position
- Downhill running
- Hard shoes.Excessive wear on the outside heel edge of a running shoe
- Hard surfaces
- Tightness of it band can occur in tall teenagers who has recently undergone adolescent growth spurt
- Imbalance in muscle strength and flexibility
- Inadequate warm-up or cool-down
- In cycling, having the feet "toed-in" to an excessive angle
- Running up and down stairs.
Sign and Symptoms
- Pain, tenderness, swelling, warmth and redness at the iliotibial band about 2 cm above the joint line and may travel up or down the thigh or leg.
- Initially pain at the beginning of an exercise that lessens once warmed up, eventually pain through out the activity. It may cause the athlete to stop in the middle of training or competition.
- Pain that worse with running downhill or stairs.
- Possibly crepitation when the tendon or bursa is moved or touched.
- Pain is often exacerbated by repetitive flexion-extension movements.
LINDENBERG classified IT band friction syndrome into 4 grades-
- a)Pain comes after running but does not restrict distance or speed.
- b)Pain comes on during running but does not restrict distance or speed.
- c)Pain comes on during running and restricts distance or speed.
- d)Pain so severe that it prevents running.
Special Tests
Thomas test
The Affected side abducts. It indicates tight ITB. Known as 'J' sign.
Obers test
Greater stretch is placed on ITB when the knee is extended
Noble's test (also known as Noble's Compression test)
Put the patient in a supine position. Next bring the affected knee up to a 90 degree knee flexion and apply pressure with your thumb to the lateral femoral epicondyle. The leg is then extended slowly. When it is extended to approximately 30 degrees, the iliotibial band translates anteriorly over the lateral femoral epicondyle under the examiners thumb.
If the patient indicates pain at this 30 degree angle, which is similar to when the patient is active, the test is considered positive and it suggests the presence of iliotibial band syndrome.
Physiotherapy Management Of Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome
1-The initial inflammation responds to anti-inflammatory medications and rest from flexion-extension activity of the knee.
2-Avoid downhill running and stairs. Use soft running shoes.
3-Icing for initial inflammation.
4-ultrasonic therapy to reduce inflammation.
5-LASER therapy
6-TENS for pain relief.Massage to prevent adherent scar.
7-When limited range of motion is identified it band stretch is given.
8-Strengthening exercises in open and closed kinematic chain.
9-Gait re-education.
10-Use lateral wedge in the shoes, for patients with it band tightness.
11-If the patient does not respond then steroid injection can be given. Surgery to remove the inflamed bursa or inflamed iliotibial band is considered usually after at least 6-12 months of conservative treatment.
What Other Visitors Have Said
Click below to see contributions from other visitors to this page...
IT Band stretch 




5 Best Iliotibial Band Stretches
1) Standing Iliotibial Band Stretch
The patient stands perpendicular to and 2–3 feet from …
Return from Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome to home page
Return from Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome to sports physical therapy
Recent Articles
|
Author's Pick
Rating: 4.4 Votes: 252 |
References
- Orchard JW, Fricker PA. Biomechanics of IT band friction syndrome in runners. Am J Sports Med. 1996 May-Jun;24(3):375-9.
- C. A. Noble. The treatment of iliotibial band friction syndrome. Br J Sports Med. Jun 1979; 13(2): 51–54. [PubMed]
- Fredericson M, Weir A. Practical management of IT band friction syndrome in runners. Clin J Sport Med. 2006 May;16(3):261-8.
- Iliotibial band syndrome. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia