Enhance your health with free online physiotherapy exercise lessons and videos about various disease and health condition
Congenital Vertical Talus
Congenital Vertical Talus
Club Foot (image)
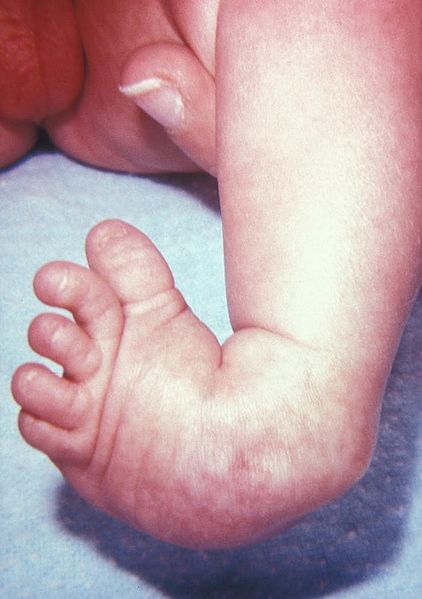 Club Foot
Club FootSynonyms
- Congenital Convex Pes Valgus
- Teratological Dislocation of Talo-Calcaneo-Navicular Joint
- Rocker bottom feet
- Congenital rigid flatfoot
- Persian Slipper foot
Definition of Congenital Vertical Talus
Vertical talus with irreducible and rigid dorsal dislocation of the navicular and equinus of the calcaneus. Characterized by rigid dorsiflexion of forefoot and fixed equinus of hindfoot.
Pathoanatomy
Congenital vertical talus is an uncommon foot deformity producing a rigid, rocker-bottom shape to the foot. The talus is vertically oriented, with dorsal displacement of the navicular. Hindfoot equinovalgus, a convex plantar surface, midfoot and forefoot dorsiflexion and abduction, and rigidity are present. Most affected children have an underlying syndrome, such as spina bifida, arthrogryposis multiplex, or a congenital or chromosomal abnormality (trisomy 18).
Differential Diagnosis
- Congenital absence of fibula
- Congenital Calcaneovalgus foot
- Planovalgus foot
- Flat foot in Cerebral Palsy
- Paralytic flat foot
- Over correction of club foot
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is confirmed radiographically with anteroposterior and lateral weight bearing or simulated weight-bearing views. A maximal plantar flexion lateral radiograph shows the inability to align the forefoot and midfoot with the hindfoot.
Treatment of Rocker Bottom feet
Treatment is similar to that for a congenital club-foot. Management principle are to re-establish normal relationship between bones of feet and hold them there. Weight bearing through 1st ray.
Conservative Management
Conservative methods of treatment are taping and use of malleable splints and serial plaster casts. Taping and malleable splints are particularly useful in premature infants until they attain an appropriate size for casting. Serial plaster casts are the major method of treatment. The technique described by Ponseti is highly effective in providing long-term satisfactory results. The use of this technique is one of the most important recent changes in pediatric orthopedics.
Surgical Management
Most infants treated by the Ponseti technique require a percutaneous tendo Achilles lengthening to correct the equinus component of the deformity. Approximately 20% later require transfer of the tibialis anterior tendon to correct dynamic supination. The need for comprehensive complete soft tissue releases is now less common.
Further Reading
- Vertical Talus . Medscape
- Vertical Talus. Orthoinfo
- CVT. Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics
- Atul Bhaskar. CVT: Treatment by reverse ponseti technique. Indian J Orthop. 2008 Jul-Sep; 42(3): 347–350.
- Aydın A, Atmaca H, Müezzinoğlu ÜS. Bilateral CVT with severe lower extremity external rotational deformity: treated by reverse Ponseti technique. Foot (Edinb). 2012 Sep;22(3):252-4.
- McKie J, Radomisli T. CVT: a review. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2010 Jan;27(1):145-56.
Return from Congenital Vertical Talus to Home Page
Recent Articles
|
Author's Pick
Rating: 4.4 Votes: 252 |

