Enhance your health with free online physiotherapy exercise lessons and videos about various disease and health condition
Coccydynia
Coccydynia simply refers to a painful coccyx. The coccyx bone is located on the end of your sacrum or tailbone and can become irritated and painful in pregnancy. This is especially evident in the final trimester due to the position of the baby and the lack of room for the baby to maneuver. Manual adjustment of the coccyx is often required and can be safely and successfully performed by the physiotherapist or chiropractor.
This condition may be referred to in various terms-
- Coccygodynia
- Coccyx pain
- Coccyaglia
- Coccygodynia
Causes of Coccyx Pain
- Coccyx pain is more common in writers and others who spend lots of time sitting, particularly on hard surfaces. Over time, the prolonged sitting can put pressure on the tailbone (coccyx), leading to inflammation and extreme pain.
- This is more common in women than men. It is usually caused by local trauma (e.g. a fall) or giving birth.
- Coccygodynia can also be caused by an injury, but it may occur seemingly spontaneously.
- On rare occasions pilonidal cysts, an infection, fractured bone or tumor can also cause pain in the coccyx.
Coccydynia symptoms may consist of one or all of the following
- Pain that is markedly worse when sitting
- Local pain in the tailbone area that is worse when touched or when any pressure is placed on it
- Pain that is worse when moving from a sitting to standing position
- Pain that is worse with constipation and feels better after a bowel movement.
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Increased pain for women, during monthly menstruation
Coccyx pain Diagnosis
Coccygodynia is commonly diagnosed based solely on the symptoms and the examination findings of local tenderness. Other conditions can be excluded by the examination and other testing (to exclude bone or tissue disorders, such as with CAT scan or MRI scan).
Conservative treatment
- Coccyx Cushion- Since sitting on the affected area may aggravate the condition, a cushion with a cut out at the back under the coccyx is recommended.
- Stool softener- If there is tailbone pain with bowel movements, then stool softeners and increased fiber in the diet may help.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs- For prolonged cases, anti-inflammatory or pain-relieving drugs may be prescribed.
- Local nerve blocks- Local nerve blocks are often beneficial.
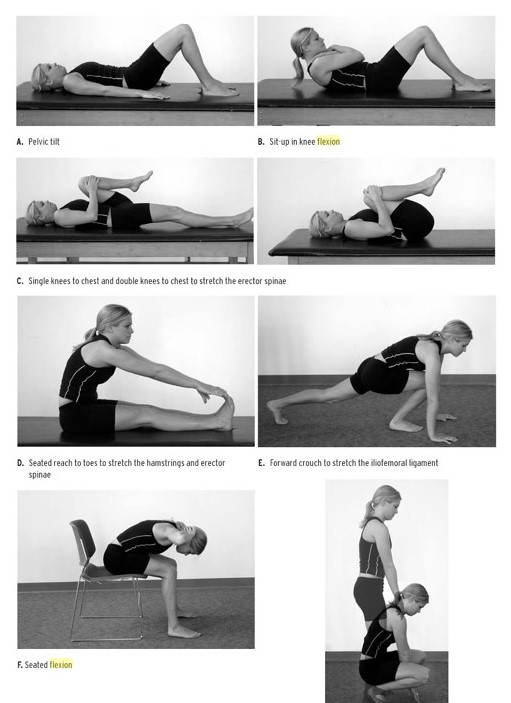
- Manual adjustment of the coccyx- Manual adjustment of the coccyx is often required and can be safely and successfully performed by the physiotherapist or chiropractor.
- postural adjustments
Surgical treatment
Rarely, when patients have unrelenting pain, a surgical resection of the coccyx (coccygectomy) may be required. Typically, surgery is reserved for patients with cancer (malignancy) or those whose tailbone pain has failed to respond to nonsurgical treatment (such as medications by mouth, use of seat cushions, and medications given by local injections done under fluoroscopic guidance).
Further Reading
- Tailbone pain. NHS Choices
- Coccyx Pain. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
- Tailbone Pain. MedicineNet
- Tailbone Pain. Spine Health
- Wray CC, Easom S, Hoskinson J. Coccydynia. Aetiology and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991 Mar;73(2):335-8.
- Lesley Smallwood Lirette, MD, Gassan Chaiban, MD, Reda Tolba, MD, and Hazem Eissa, MD. An Overview of the Anatomy, Etiology, and Treatment of Coccyx Pain. Ochsner J. 2014 Spring; 14(1): 84–87.
- Coccygodynia. Physiopedia
Return from Coccydynia to Orthopedic Physiotherapy
Return from Coccydynia to Home Page
Recent Articles
|
Author's Pick
Rating: 4.4 Votes: 252 |

